Income Tax Calculation for Salaried Employees: Explained with Examples
Learn how to calculate income tax on salary with simple examples under both the old and new tax regimes in India. A clear guide for salaried individuals
Filing income tax may seem overwhelming, especially when it comes to calculating how much you owe. But with a clear understanding of the process and current tax slabs, you can easily figure it out. This guide is designed to help salaried individuals understand how to calculate income tax on their salary—with real-life examples, for both the old and new tax regimes.
Understanding the Basics of Income Tax
Income Tax is the tax you pay on your income to the Government of India. As a salaried employee, your employer deducts Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) based on your estimated income. You are required to file your Income Tax Return (ITR) annually to declare your income and claim eligible deductions or refunds.
Income Tax Slabs for FY 2024–25
1. Old Tax Regime
(Deductions like 80C, 80D, HRA, etc. are applicable here.)
2. New Tax Regime (Default regime from FY 2023–24)
(Most exemptions and deductions are not allowed, except standard deduction and NPS employer contribution.)
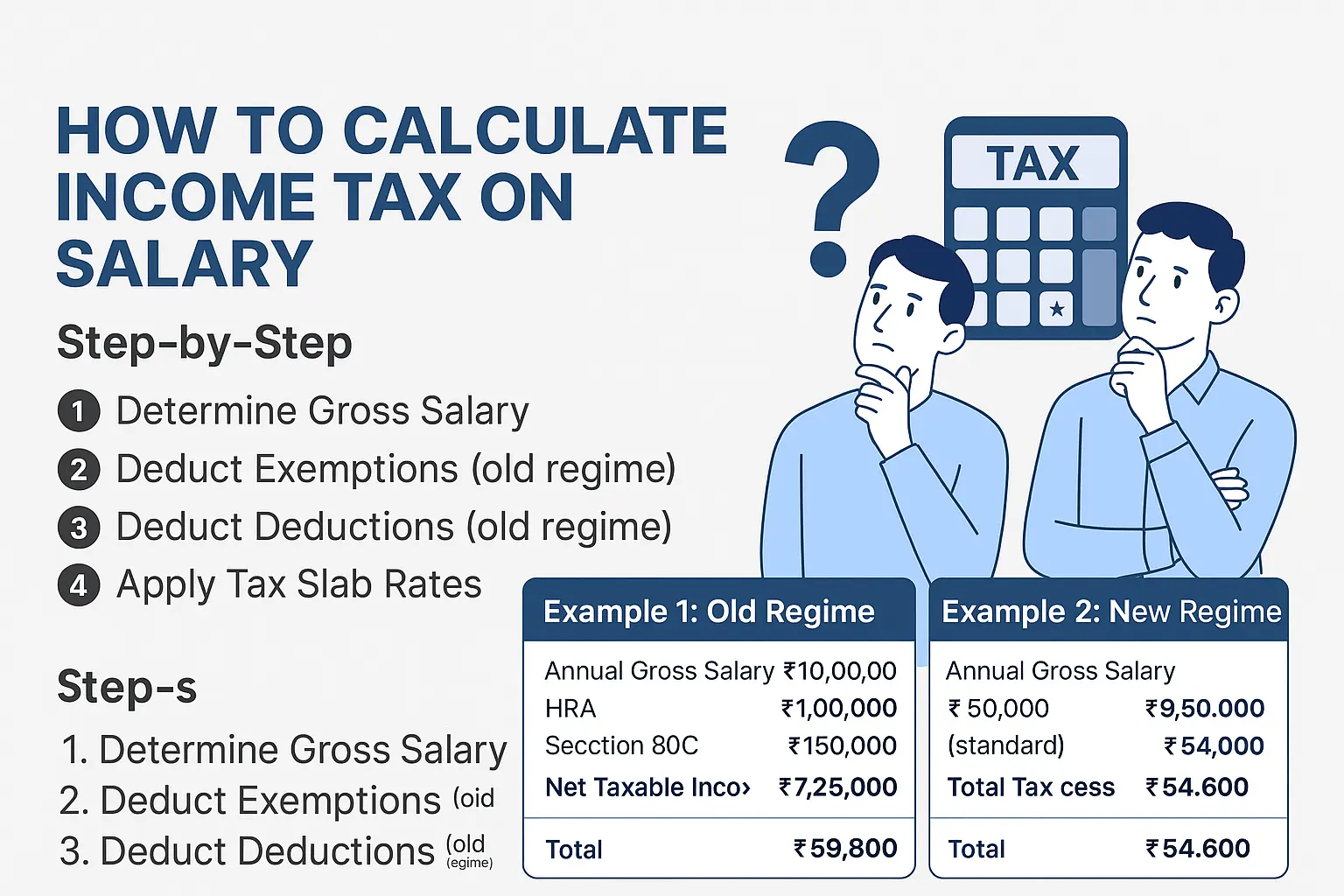
How to Calculate Income Tax on Salary: Step-by-Step
Let’s break down the calculation process under both tax regimes.
Step 1: Determine Gross Salary
This includes:
- Basic salary
- House Rent Allowance (HRA)
- Special allowance
- Bonuses
Step 2: Deduct Exemptions (if opting for old regime)
Examples include:
- HRA (under Section 10(13A))
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
Step 3: Deduct Deductions (Old regime only)
- Section 80C: Up to ₹1.5 lakh (PF, LIC, ELSS)
- Section 80D: Health insurance premiums
- Section 24(b): Home loan interest (₹2 lakh)
Step 4: Apply Tax Slab Rates
Based on taxable income, use the relevant slab to compute tax.
Step 5: Add Cess
A 4% health and education cess is added to the total tax payable.
Example 1: Income Tax Calculation Under Old Regime
Annual Gross Salary: ₹10,00,000
- HRA exemption: ₹1,00,000
- Section 80C deduction: ₹1,50,000
- Section 80D deduction: ₹25,000
Net Taxable Income = ₹10,00,000 – ₹1,00,000 – ₹1,50,000 – ₹25,000 = ₹7,25,000
Tax Calculation:
- 0 – 2.5L: Nil
- 2.5L – 5L: 5% of 2.5L = ₹12,500
- 5L – 7.25L: 20% of 2.25L = ₹45,000
- Total = ₹57,500 + 4% cess = ₹59,800
Example 2: Income Tax Calculation Under New Regime
Annual Gross Salary: ₹10,00,000
- Standard deduction: ₹50,000 (only deduction available)
Net Taxable Income = ₹10,00,000 – ₹50,000 = ₹9,50,000
Tax Calculation:
- 0 – 3L: Nil
- 3L – 6L: 5% of 3L = ₹15,000
- 6L – 9L: 10% of 3L = ₹30,000
- 9L – 9.5L: 15% of 0.5L = ₹7,500
- Total = ₹52,500 + 4% cess = ₹54,600
As you can see, depending on your salary and deductions, either regime may result in lower tax.
Choosing the Right Tax Regime for You
As evident from the examples, the choice between the old and new tax regimes is highly individual and depends largely on your financial situation and investment habits.
- Opt for the Old Tax Regime if:
- You claim significant exemptions like HRA and LTA.
- You make substantial investments in tax-saving instruments (80C, NPS under 80CCD(1B)).
- You are repaying a home loan and claim interest deductions (Section 24(b)).
- You incur considerable expenses on health insurance premiums (80D).
- Essentially, if your total deductions and exemptions reduce your taxable income significantly enough to outweigh the lower tax rates of the new regime.
- Opt for the New Tax Regime if:
- You have fewer exemptions and deductions to claim.
- You prefer a simpler tax filing process with minimal documentation.
- You are an individual with a taxable income up to ₹7 lakh, as the Section 87A rebate makes your tax liability zero in this regime.
- You are an individual with higher income but do not utilize many tax-saving options, as the lower tax rates at various income levels might be more beneficial.
Important Note: Salaried employees can choose their preferred tax regime at the beginning of the financial year by declaring their choice to their employer for TDS purposes. If you don't make an active choice, the new tax regime will be applied by default for TDS purposes. However, you can make the final choice or change your option at the time of filing your Income Tax Return. It's advisable to perform a comparison calculation for your specific scenario before making a final decision.
Understanding Form 16
Your employer provides you with Form 16 at the end of the financial year (typically by June 15th). This is a crucial document that details your salary income, the deductions claimed (based on your declaration to the employer), and the Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) by your employer. It serves as proof of income and tax paid and is essential for filing your Income Tax Return (ITR). Ensure all details in Form 16 match your own records.
Tips for Efficient Income Tax Filing
- Collect your Form 16 from your employer
- Use Form 26AS to check TDS
- Use AIS/TIS for additional information
- Claim deductions accurately
- File before the due date to avoid penalties
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate income tax helps salaried employees make smarter financial decisions. Whether you prefer the old regime with deductions or the simplified new regime, it’s crucial to do your calculations carefully. Use the examples and tips above to plan better, file accurately, and avoid surprises.
Need more help with tax filing or financial tools? Explore smart business finance solutions at EximPe—your trusted growth partner.
FAQs on How to Calculate Income Tax
1. How to calculate income tax on salary with example?
Refer to the examples above based on ₹10 lakh salary under both tax regimes.
2. What is the easiest way to calculate income tax?
Use an online income tax calculator by entering your income, exemptions, and deductions.
3. How to calculate income tax in new regime?
Subtract the standard deduction from gross salary, and apply the new regime tax slabs.
4. Is standard deduction allowed in the new tax regime?
Yes, from FY 2023–24, salaried individuals can claim ₹50,000 even in the new regime.
5. Can I switch between old and new regimes every year?
Yes, salaried individuals can choose their regime every financial year while filing ITR.
6. Which tax regime is better?
It depends on your income and deductions. If you claim many deductions, the old regime may be better.
7. How is cess calculated on income tax?
A 4% cess is levied on the total tax amount, not on income.
8. What is included in taxable salary?
Basic pay, HRA, special allowances, bonuses, and any other taxable components.
9. What deductions are not allowed in the new regime?
Deductions under Sections 80C, 80D, 80G, 24(b), and most others are not allowed.
10. How can I reduce my tax liability?
Use deductions under the old regime, invest in tax-saving instruments, or evaluate the benefits of the new regime.